SnapshotNIR guides HBOT treatment for a necrotic facial wound leading to full wound closure
Dr. Tyler Sexton, MD, MAPWCA
Case details
In this case study, a 56-year-old female patient was treated by Dr. Tyler Sexton and his team for the management of osteoradionecrosis (ORN) of the mandible, secondary to radiation therapy. The patient presented with severe ongoing pain and tissue breakdown around the jaw, having lost multiple teeth and upper lip tissue. Past interventions, including nasal ablation, failed to improve her symptoms.
Dr. Sexton utilized near-infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) with SnapshotNIR to guide his management plan, which included hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT), and potential additional surgical interventions if required.
In March 2025, SnapshotNIR was used to capture a baseline tissue oxygen saturation, which demonstrated hypoxia near the necrotic area and lower aspect of the patient’s face. The patient had no viable tissue on the right side of the nose and upper lip with poor definition, and missing teeth.
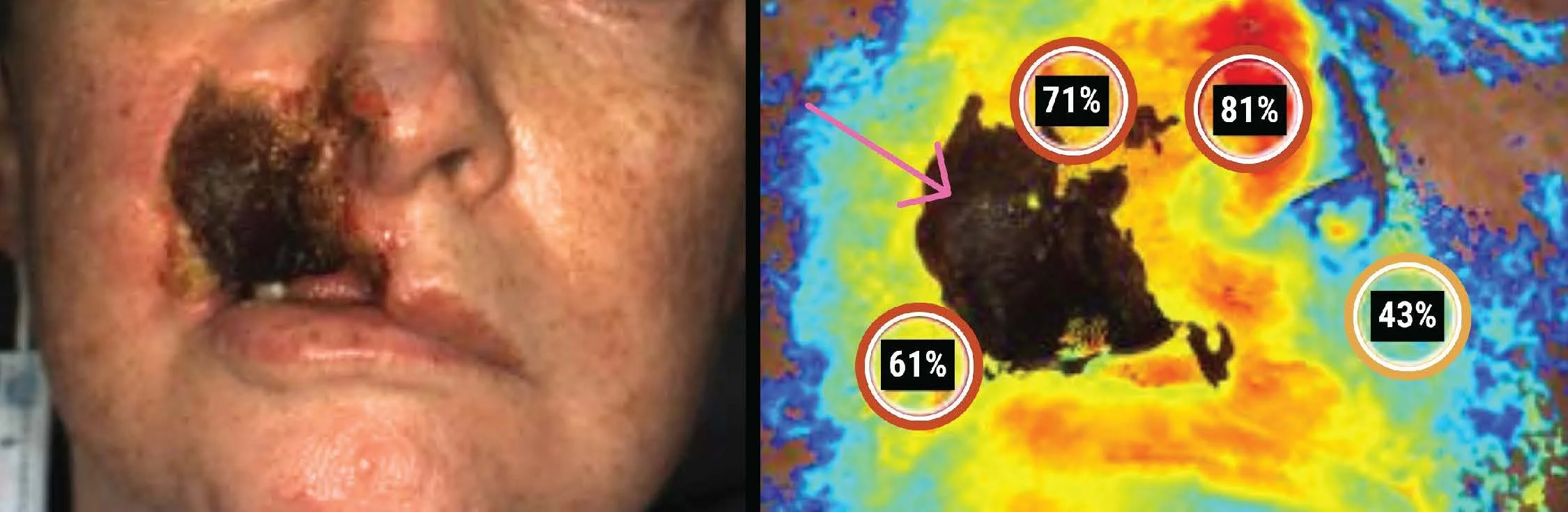
Image 1. Baseline, March 27, 2025, clinical image (left) and StO2 image (right) from SnapshotNIR. Markers read 61%, 71%, 81%, and 43% in the surrounding tissue. There is extensive necrotic tissue present in the region of interest (pink arrow).
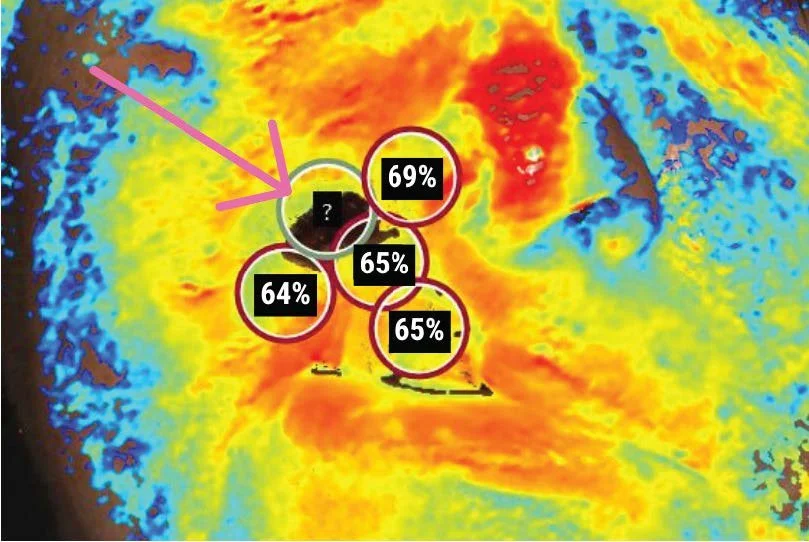
Image 2. April 16, 2025. StO2 image from SnapshotNIR after seven HBO sessions which showed increased StO2 (65%, 68%, and 71%), and a significant reduction of necrotic tissue in the region of interest (pink arrow).
Treatment planning with SnapshotNIR
Alongside pharmacology to manage pain, improve microcirculation, and support healing of irradiated tissue, the patient was prescribed HBOT under the Marx Protocol. Pre-operatively, with the goals of reducing the progression of necrotic tissue and enhancing vascular regeneration, the plan was to have the patient undergo twenty HBOT sessions.
Serial Imaging with SnapshotNIR
The patient’s response to HBOT was monitored using SnapshotNIR to confirm efficacy of the intervention, track signs of necrosis, and watch for signs of infection. After seven sessions over 2.5 weeks, drastic improvements were observed on re-imaging.
Using SnapshotNIR data to confirm completion of HBOT
Having confirmed intervention effectiveness with SnapshotNIR, the patient continued with HBOT for an additional two weeks, completing another ten sessions. Follow-up tissue oxygenation images showed normalizing values compared to the surrounding skin, an improvement from baseline, and elimination of necrotic tissue.
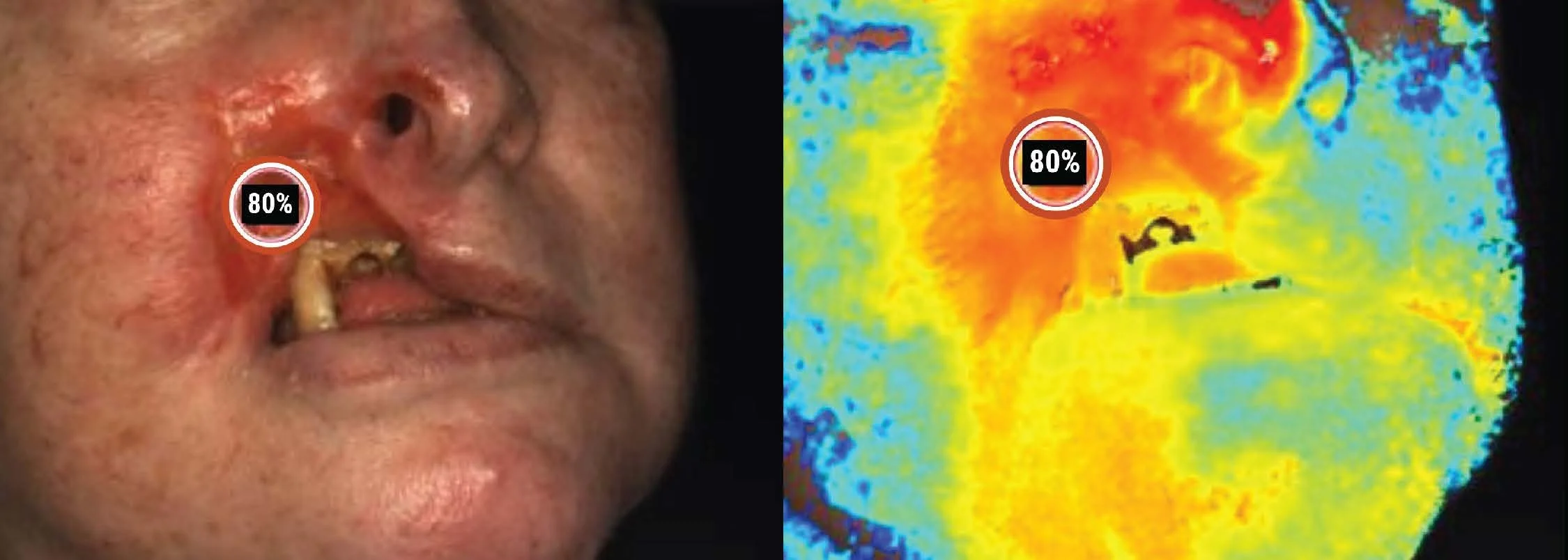
Image 3. April 30, 2025 following 17 HBO sessions. Clinical image (left) and StO2 image (right) from SnapshotNIR. With minimal-to-no necrotic tissue present, the StO2 marker reads 80% in the area of interest.
The Impact of SnapshotNIR
“SnapshotNIR findings validated our clinical judgment regarding impaired perfusion but also revealed more detailed, localized deficits than what were appreciated on visual inspection alone. It confirmed the suspected need for adjunctive oxygenation and allowed for more precise wound mapping, reinforcing the use of HBOT. It added a quantifiable dimension to ongoing wound surveillance not achievable through visual exam alone.”
SnapshotNIR device showing the side-by-side comparison images on April 16 2025, after seven HBO sessions. Side-by-side comparison allows the clinician to view the tissue oxygen saturation while seeing the patient’s color image of their wound.
The Plan of Care (PoC) for this patient was supported by serial SnapshotNIR imaging. Baseline imaging identified hypoxic tissue, and helped distinguish between viable and non-viable tissue, guiding debridement interventions prior to HBOT, and aiding in monitoring HBOT efficacy.
Objective data from SnapshotNIR supported the clinical decision to delay a premature surgical referral, encouraging a conservative management plan. Through serial imaging, a rapid increase in oxygenation was observed in the region of interest, seen in the table below, providing the clinicians with confidence in the treatment plan.
Positive Patient Outcomes using SnapshotNIR
The patient was able to visualize the wound healing trends through repeated imaging with SnapshotNIR, which improved engagement, trust, and adherence to the care plan. This transparent feedback loop helped build confidence, reduce psychological distress, and reinforce the clinical value of HBOT. The care team was also able to avoid false-negative surgical assumptions, preserve tissue, and improve healing potential.
The expected outcome was surpassed, as the patient had conversations with an oral/maxillofacial surgery team in case the need for surgery arose. Through dedicated treatment, the patient experienced:
Improved tissue oxygenation
Reduced eschar
Decreased need for surgical debridement
Preserved facial tissue
Avoidance of surgical intervention
Improved quality of life and symptoms
“SnapshotNIR supported our clinical decision to pursue conservative management, eliminating a potential costly escalation. Communication between our team, surgical staff and the patient was clear and concise, as the objective data from the images visually demonstrated our reasoning. This patient underwent targeted HBOT and was able to experience better functional recovery, and fewer complications as a result.”
Thank you to Dr Sexton and his clinical team for this case study.
Dr. Tyler Sexton is the Chief Medical Officer (CMO) at Brevard Regional Hyperbaric Center Melbourne Florida; CMO, UrgentFlex Orlando Fl; CMO, TrueHyperbarRx , Orlando, Fl; CMO, Coastal Hyperbarx Ocean Springs, MS; and CMO, Precision Hyperbarics, Tampa, Fl.