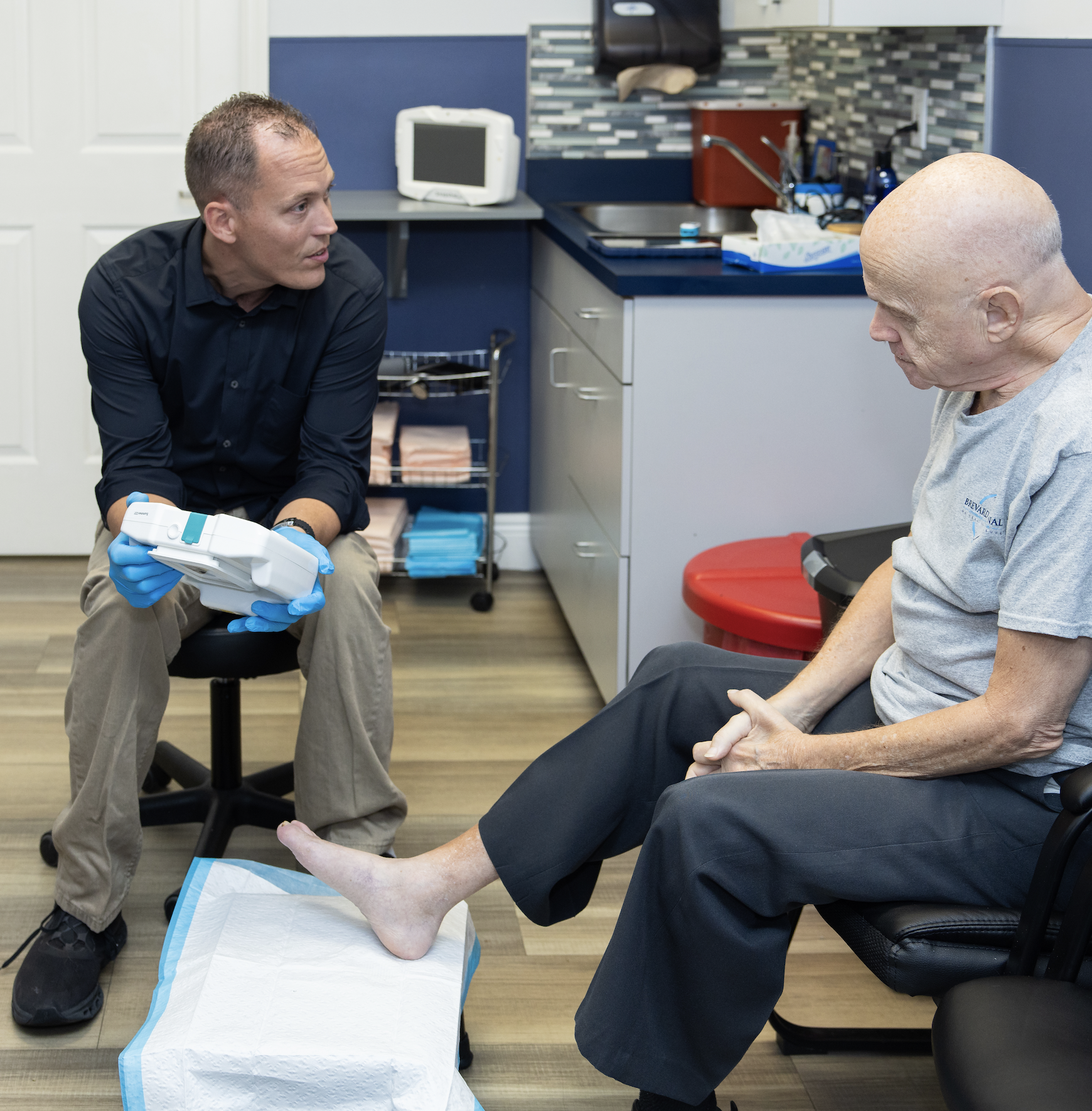
Precision bacterial autofluorescence imaging.
Track and document actionable data for medical necessity, therapeutic efficacy, and outcomes while easily integrating digital captures into the patient record with SnapshotGLO.
SnapshotGLO Applications
Detect
Reveal what the eye cannot see to drive targeted care from the start.
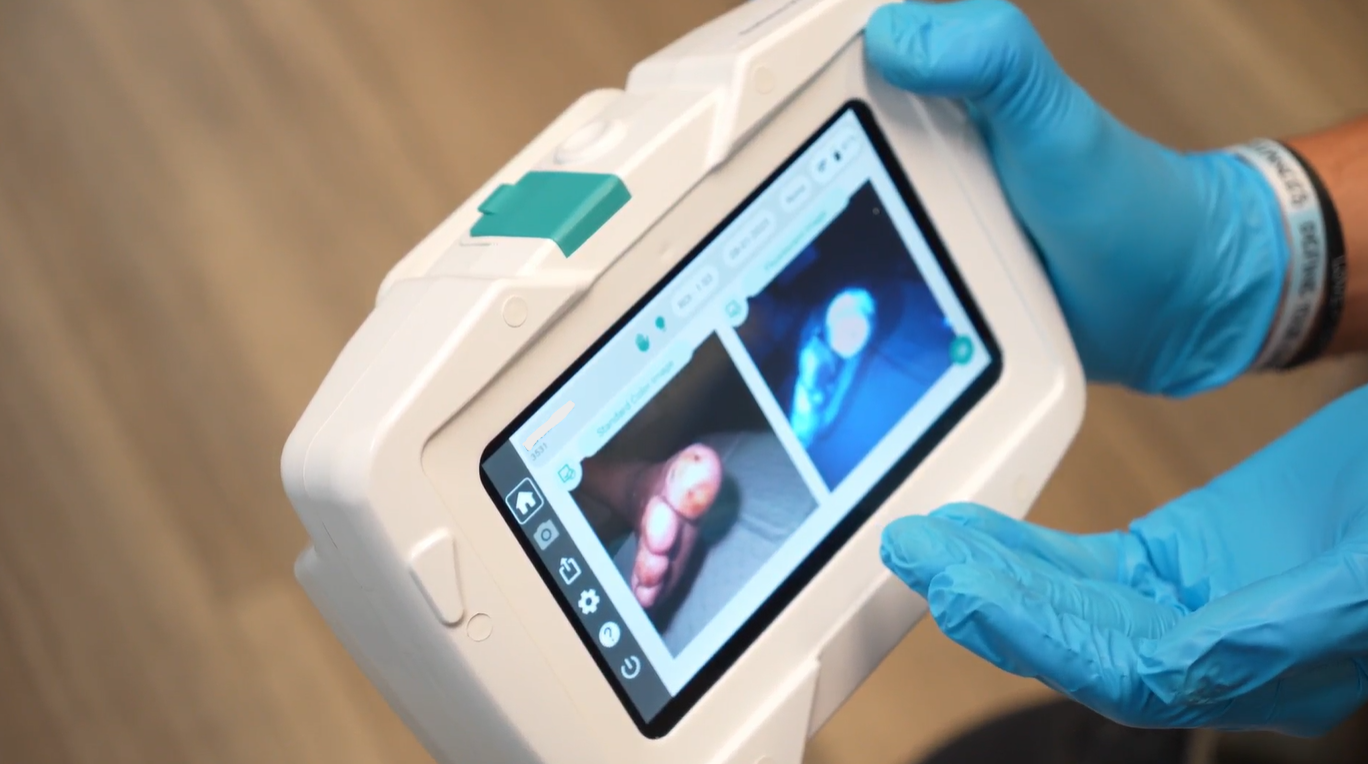
SnapshotGLO uses concentrated ultra-violet light to non-invasively detect elevated bacterial loads at the point of care.
Direct
Guide clinical decisions with confidence and clarity.
SnapshotGLO imaging allows real-time assessment to support clinical decision-making and effective, evidence-driven interventions.
Protect
Safeguard patient well-being and objectively document clinical decisions.
SnapshotGLO aids providers in adhering to the fundamental principle that guides patient well-being and medical ethics: ‘first, do no harm’. Any open wound is at risk for developing complications, and the ability for providers to identify the most effective treatment for the individual patient can assist with enhancing and fostering earlier healing.
SnapshotGlo in Wound Assessment
Visualize bacterial bioburden
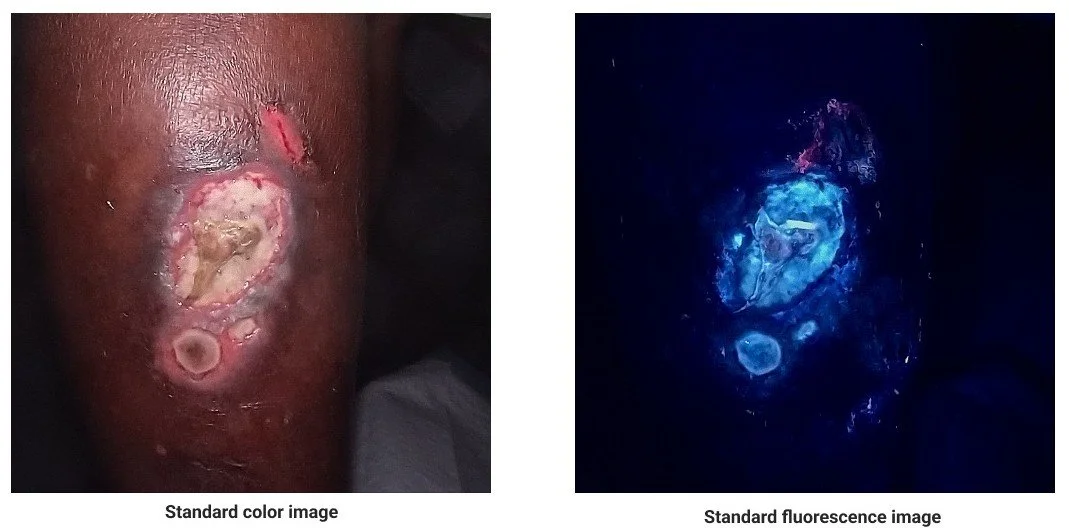
SnapshotGLO gives clinicians immediate, actionable insight into bacterial presence—right at the point of care. By using advanced autofluorescence imaging, SnapshotGLO helps reveal bacterial bioburden in ways that traditional assessment methods often miss. SnapshotGLO visualizes the presence and extent of bacterial bioburden in real time, highlighting concerns across the wound bed, peri-wound, and surrounding tissue—areas frequently overlooked with standard assessment techniques.
assist in targeted sampling
With clear visual cues, clinicians know exactly where to sample, helping improve swab accuracy and enhance the effectiveness of techniques like Levine sampling, which typically captures only the wound center and may underrepresent true bacterial load. SnapshotGLO points to areas that matter most, ensuring a more complete and informative assessment.
By visualizing bacterial hotspots instantly, SnapshotGLO empowers clinicians to intervene sooner and more precisely—supporting improved decision-making and potentially contributing to reduced infection risk.
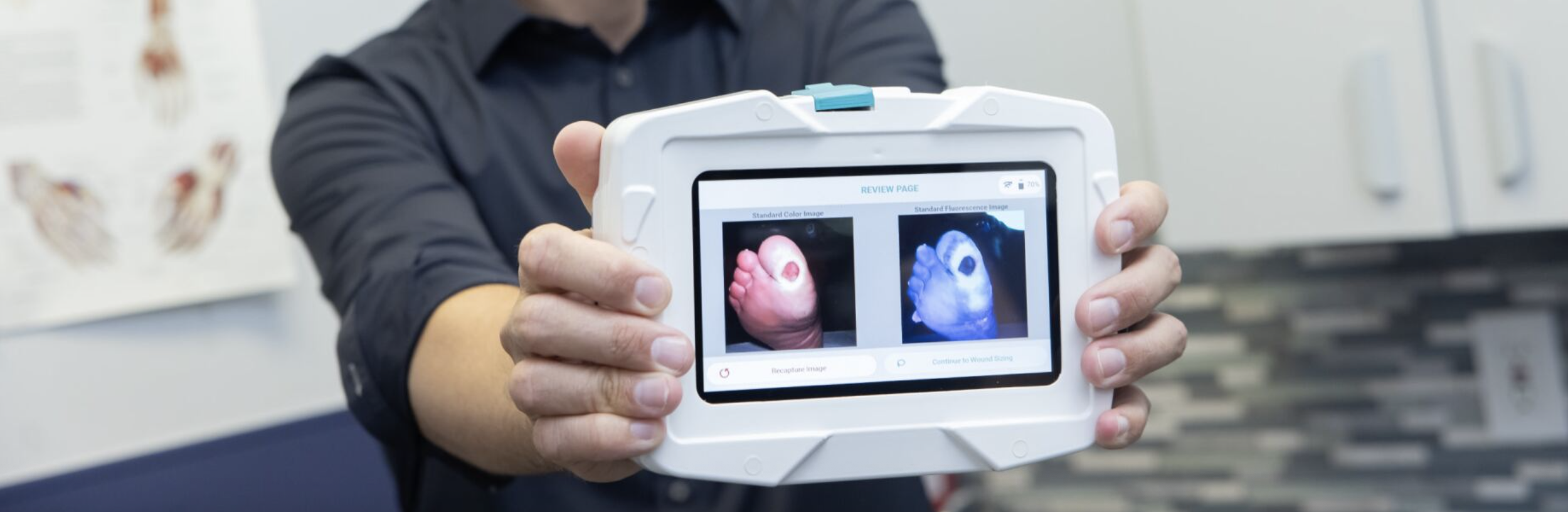
See how SnapshotGLO can be used to identify elevated bacterial bioburden.
By illuminating areas of elevated bacterial load, SnapshotGLO helps clinicians make more informed decisions about treatment, such as debridement or the need for antimicrobial intervention. This targeted approach guides more efficient infection management, ensuring effective wound bed preparation. With real-time, easy‑to‑interpret imaging, SnapshotGLO empowers care teams and providers to address bacterial issues earlier in the wound‑care process—helping protect patients, support healing progress, and reduce the likelihood of complications.
SnapshotGlo in Wound CARE
Targeted Debridement
By visualizing harmful bacteria, SnapshotGLO guides clinicians to complete a more thorough and accurate debridement when clinically appropriate.
By clearly differentiating between areas of high bacterial load and healthy tissue, SnapshotGLO helps ensure that interventions remain focused, conservative, and patient‑centered.
Using SnapshotGLO to help guide debridement techniques can help improve treatment effectiveness and wound be preparation. Read more:
Using bacterial autofluorescence pre- and post-debridement of a surgical site
Pre-debridement image. (Clinical + Bacterial autofluorescence)
Post-debridement image. (Clinical + Bacterial autofluorescence)
Hear from Dr. Tyler Sexton, MD, on using SnapshotGLO in his wound care practice.
Precise Infection Control
As part of a clinician’s workflow for infection prevention, antimicrobials and antibiotic stewardship are often necessary steps. Use SnapshotGLO to aid in:
Locating areas of highest bacterial concentration to ensure reliability of wound culture results
Optimal wound cleansing and treatment via guided antiseptic and dressing selection
Selection of appropriate antibiotic(s) when indicated
Watch this video to see SnapshotGLO identify cyan and red autofluorescence indicating different types of bacteria.