Surgical Debridement and Documentation for Chronic Wounds with SnapshotNIR
Detect, Direct and Protect
Chronic wound care often faces increased scrutiny due to high utilization and costs. For advanced wound care procedures like surgical debridement, it’s critical to have robust wound documentation to support medical necessity and reduce the risk of claim denials. SnapshotNIR, a diagnostic-driven near-infrared medical imaging tool, enhances documentation while supporting better clinical decision-making.
Why does Chronic Wound Debridement Require Detailed Documentation?
The Noridian LCD, Wound and Ulcer Care (2021) (1) identifies that the minority of beneficiaries will require more than 12 total surgical excisional debridements within a 360-day period, with only 5 of these involving removal of muscle/fascia and/or bone. While Noridian does not present this as a hard cut off, the burden is on the provider to show medical necessity to continue these more extensive debridements.
Use SnapshotNIR to detect, direct and protect before, during and after your patient interaction.
Start with imaging.
Take a baseline image of the patient
Ask yourself, “Why this intervention for this patient?”
Hint: It should never be about the $$$
Ask yourself, “What will the application frequency be?”
Ask yourself, “What other treatment modalities could be used in this situation?”
Make sure to document.
Wound or ulcer size – measure with the linear and area features on SnapshotNIR
Use serial imaging to monitor and track the wound’s healing trajectory
SnapshotNIR can help particularly with preparing a wound bed for CAMPs application, and pre- and post-debridement to support repeat debridements as required
Case Example 1: Leg ulcer pre- and post-debridement and documentation options using SnapshotNIR
Pre-debridement with SnapshotNIR
Scattered red and orange colors (indicating higher oxygenation) throughout the wound and peri-wound
Lighter colors in the deoxyhemoglobin panel, suggesting suboptimal venous flow
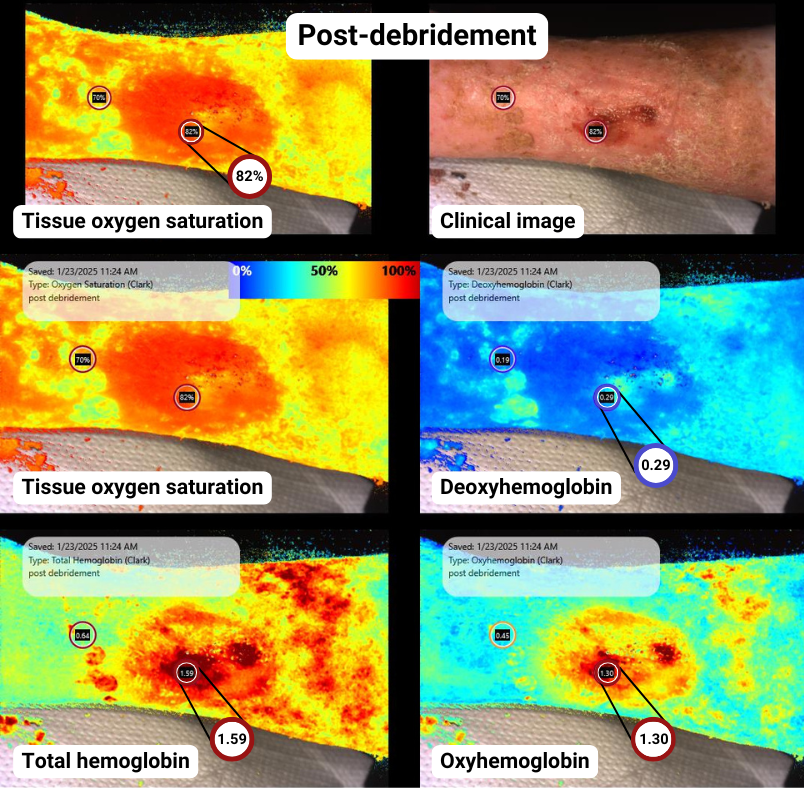
Post-debridement with SnapshotNIR
Deeper and broader red and orange indicating higher tissue oxygen saturation across the wound and peri-wound
Significant increase in oxyhemoglobin, with a decrease in deoxyhemoglobin indicating a healing wound trend
Case Example 2: Pre- and post-debridement with a focus on hemoglobin trends to monitor chronic wound healing
Pre-debridement with SnapshotNIR
Low StO2 areas in the wound bed
High deoxyhemoglobin and low oxyhemoglobin
Indicating a non-healing wound trend
Post-debridement with SnapshotNIR
StO2 increased by 10% in some areas
Large increase in oxyhemoglobin and total hemoglobin (resulting in a slight increase in deoxyhemoglobin)
Indicating a healing trajectory
enhance your Wound Documentation with SnapshotNIR
These images, alongside patient treatment notes, can be integrated into the patient’s profile to support clinical decision-making. Across standard and advanced wound care interventions, SnapshotNIR supports chronic wound debridement by assisting in clinical decision-making and enhancing chronic wound documentation. Its imaging capabilities provide supportive evidence to demonstrate medical necessity to payors during appeals, reviews, and audits.
About SnapshotNIR: SnapshotNIR, developed by Kent Imaging, is a medical imaging device using near-infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) to image tissue oxygenation, oxyhemoglobin, deoxyhemoglobin and total hemoglobin. For a first-hand look at the advantages of NIRS technology in wound imaging, visit our webinars page, here.