How Does Imaging Technology Aid in Reconstructive Surgery?
With the click of a button, SnapshotNIR helps you to assess tissue viability in the microvasculature and plan the most appropriate treatment pathway. Using NIR light, SnapshotNIR is non-invasive and useful in multiple wound care and surgical settings providing valuable point-of-care imaging information to physicians and nurses to reduce complications and predict tissue viability. In the field of reconstructive surgery, many complications in wound healing can arise, one of them being flap necrosis.
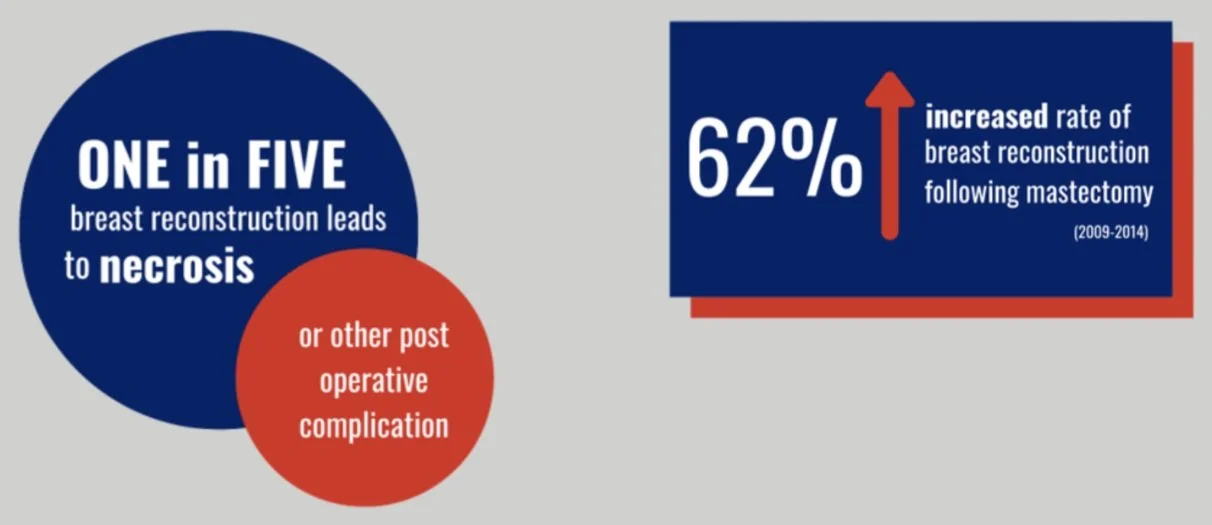
A common example of flap necrosis is following breast reconstruction. One in five breast reconstructions leads to necrosis or other post-operative complications. (Source: JAMA Surg. 2018;153(10):901-908. doi:10.1001/jamasurg.2018.1687 Published online June 20, 2018.) During surgery, a flap of tissue is taken from the abdomen or latissimus and in some instances, the tissue may not get enough blood circulation and may die. This is called "necrosis." Due to the expensive costs of ICG fluorescence angiography, many surgeons rely on surface tissue visuals alone. Yet poorly oxygenated skin flaps are often not clinically apparent until hours after surgery, at which point, they are more difficult to salvage and may have additional complications. SnapshotNIR, without the need for dyes, injections, or direct patient contact, helps to detect tissue viability issues in skin flaps earlier, allowing clinicians to intervene more quickly, helping to reduce complications and manage healthcare costs.
“SnapshotNIR has helped our team to evaluate flaps throughout the entire care continuum: pre-operative planning, perforator identification, flap design, and post-operative monitoring on the OR floor and in the office.” - Dr. C. Rammos, MD PSG Plastic Surgery
The goal of the SnapshotNIR device is to improve outcomes and reduce complications in reconstructive surgery by going beyond the surface of the skin. The point-of-care imaging approach represents the highest level of interaction between the healthcare provider and patient.
• Cost-effective. SnapshotNIR is sensibly priced with no required consumables and can be used at all stages of the patient’s care with no additional fees.
• Accurate information. Use SnapshotNIR to help determine the preoperative plan, make decisive intraoperative surgical decisions, monitor flaps, and document healing postoperatively.
• Efficient speed of capture. SnapshotNIR images are captured and displayed in under 10 seconds, with no limitation on the number of images captured.
• Confirm clinical judgment. With SnapshotNIR, staff can capture images with minimal disruption to the patient’s care in the PACU and on the floor, helping to confirm any suspicions of concerning tissue throughout the continuum of care.
Understanding skin flap blood flow is critical in reducing complications. SnapshotNIR provides reliable tissue oxygenation assessment in a compact, highly affordable device. With this portable footprint, SnapshotNIR brings point-of-care imaging to “every” surgeon, providing non-invasive monitoring that can be done anywhere.
For clinical examples of how SnapshotNIR was able to improve patient outcomes post-surgery, we recommend reviewing the following case studies and publications:
Bilateral skin-sparing mastectomy with immediate DTI reconstruction [PDF] - Dr. Glyn Jones, MD
Snapshot Multispectral Imaging Is Not Inferior to SPY Laser Fluorescence Imaging When Predicting Murine Flap Necrosis – PRS Journal [PDF] Glyn Jones, MD, et all.
The Use of Multispectral Imaging in DIEP Free Flap Perforator Selection: A Case Study – PRS Global Open [PDF] Charalambos K. Rammos, MD, et all.
Bilateral skin-sparing mastectomy with immediate DTI reconstruction
Dr. Glyn Jones, MD
The area of concern noted by SPY regarding flap viability is demarcated by the surgical marker and the incision line on both the right and left breasts. The NIRS images (bottom) of each breast illustrates adequate tissue oxygenation in these zones, providing additional insight to the surgeon to proceed with the planned reconstruction.